Blood
To better understand leukemia, you need to first understand a bit about blood, what it does and how it is made.
- Blood is pumped around your body by your heart and travels around in vessels called arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from your heart to the tissues in your body. Veins carry blood from your tissues back to your heart.
- Your heart, blood and blood vessels form the circulatory (say: sir-koo-LATE-or-ee) system.
- Blood is made of different kinds of cells that float in liquid called plasma.
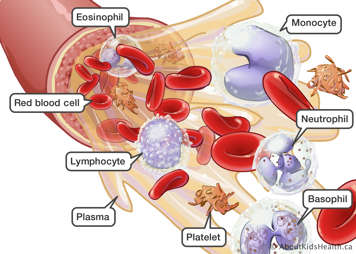
Blood cells
There are three main types of blood cells.
- Red blood cells make up half of the blood cells in normal blood. These cells carry oxygen from the lungs.
- Platelets are small cells that stop your body from bleeding when you get hurt.
- White blood cells are part of your immune system and work to keep your body healthy by fighting diseases or infections from things like bacteria or viruses. There are a few types of white blood cells, each with different jobs.
Blood cells have a short life span. Your body needs to constantly make new ones to replace blood cells that are old and worn out.
Haematopoiesis (making new blood cells)
Your body makes new blood cells through a process called haematopoiesis (say: hee-mah-tuh-poe-EE-sis).
Haematopoiesis happens in our bone marrow. The bone marrow is a spongy material found on the insides of the big bones in our body. You can think of bone marrow as a blood cell factory. All the different types of blood cells are made there. Healthy bone marrow makes millions of blood cells every day. This is why bone marrow tests are used to find out if you have leukemia.
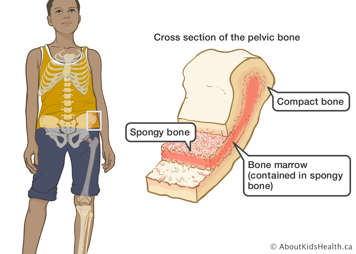
White blood cells
White blood cells help fight infection. There are two main types of white blood cells.
- Lyphoid (say: lim-foyd) cells mature or specialize into a kind of white blood cell called a lymphocyte (say: lim-foe-site).
- Myeloid (say: my-uh-loyd) cells mature or specialize into certain types of cells, including neutrophils.
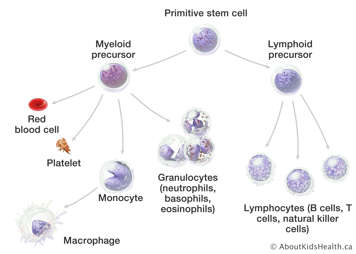
When the blood cells have specialized to form mature blood cells, they are let out of the bone marrow and into the blood to circulate around the body.
What is leukemia
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood cells in the bone marrow. In leukemia, there is a mutation in the DNA of an immature blood cell, called a stem cell. Because of the mutation, the blood cell divides out of control to make many more immature blood cells called blasts. As more and more leukemic blasts are formed, they fill up the bone marrow and start leaking out into the bloodstream. Having so many leukemic blasts in the bone marrow means it’s hard to make healthy blood cells. So, most of the time people with leukemia have low numbers of all normal blood cells – low normal white cells, low platelets and low red blood cells.
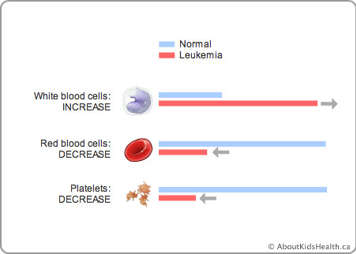
Here are some differences between people with healthy bone marrow and people with leukemia:
| People with healthy bone marrow | People with leukemia |
|---|---|
| Have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to all the cells in their body | Do not have not enough red blood cells to carry oxygen; they look pale and feel tired and short of breath. This is called anemia (say: a-nee-mee-yah). |
| Have enough platelets to stop bleeding when injured | Do not have enough platelets; they bleed or bruise very easily. This is called thrombocytopenia (say: throm-bo-site-o-pee-nee-yah). |
| Have enough white blood cells to fight infection | Do not have enough white blood cells; they get infections very easily. This is called neutropenia (say: noo-tro-pee-nee-yah). |
There are a number of different types of leukemia, but the most common types are
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and
acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To learn more about these types of leukemia check out these sections.
How is leukemia diagnosed?
Doctors learn what type of leukemia you have through a process called diagnosis.
Usually, diagnosis of leukemia starts with a doctor doing a blood test called a complete blood count to check the number of blood cells in your blood, and see if there are too many or too few. Then the doctor will also do a bone marrow aspiration where they take a sample of your bone marrow. They will also do a lumbar puncture to see if any leukemic blasts are in your cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the fluid around your brain and your spine.
How is leukemia treated?
Doctors use the information they gather to diagnose what type of leukemia you have and plan your treatment. The main type of treatment for leukemia is chemotherapy. Rarely, other treatments such as radiation are required. The goal of treatment is to kill all of the leukemic blasts in your body. You will learn more about different types of treatment in the sections on cancer medications and cancer treatments and support therapies.
Prognosis for leukemia
Your best source of information about your leukemia is your health-care team. If you have any questions or there is anything you do not understand about your leukemia, ask your doctors and nurses. If you are nervous about asking the doctors or nurses by yourself, talk to your parent/caregiver. They may be able to answer your questions or they can help you ask questions.






