Clinic appointments are important check-ups to make sure your lungs are healthy and you are taking in enough nutrition to help you grow and thrive. You will have a clinic appointment every 3 months where you will have some routine tests or more frequently if you have any acute health problems. They are also an opportunity for you to ask questions about cystic fibrosis (CF) and learn about how to best take care of yourself. There are many different members of your CF health-care team (e.g., doctor, nurse, nurse practitioner, physiotherapist, dietitian, pharmacist, social worker and others) that can help you stay healthy.
Pulmonary function test (PFTs) or spirometry
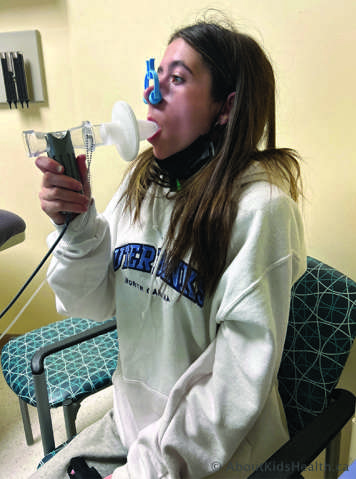
This is the “blowing test.” It measures how much and how fast your lungs can take air in and blow it out. This test is done at least every three months. It is how your health-care team monitors your lung function and health in addition to how you’re feeling.
Sputum cultures/Throat swab
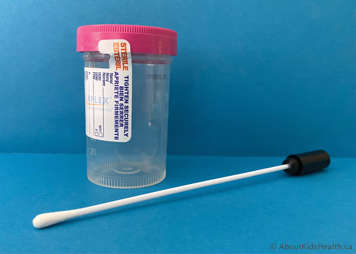
A sample of your mucus will be sent to a lab to see what bacteria are growing in it. You will either cough up some mucus (sputum sample) or a throat swab will be taken from the back of your throat. This is usually done at every clinic visit to help guide treatment if you get sick.
Sweat chloride test
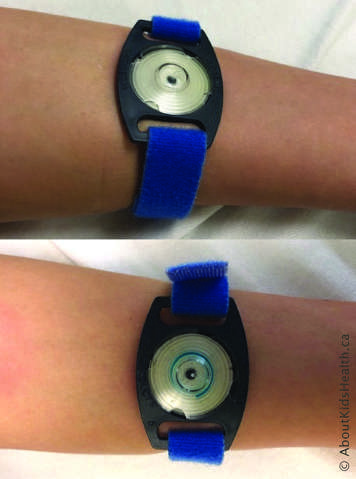
A sweat chloride test measures the amount of chloride in your sweat. It involves using an armband to collect a small amount of sweat. The test doesn’t hurt and will take about an hour to complete. This test is used to diagnose CF as well as to monitor treatment with some of the medications.
Blood tests
Blood tests are done to measure the level of blood cells, vitamins and minerals, and electrolytes in your blood as well as how your liver and kidneys are functioning. The results from these tests help your health-care team to know if you are receiving enough nutrients to help you grow.
Chest X-ray
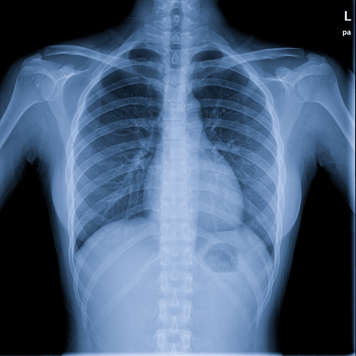
Chest X-rays will provide your health-care team with an image of your lungs.
Having chest X-rays taken over time helps your health-care team to monitor the health of your lungs to see if they are getting better or worse. They also show if there is mucus or closed-off airways in the lungs.
CT chest scans
CT scans provide more detailed pictures than X-rays of the inside of your body. A CT scan can provide more information about the health of your lungs.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to get a picture of the organs inside your body. This is done if more information about an organ, such as the liver, is needed.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
An OGTT is a test where the blood sugar levels are checked after you drink a special sugary drink to see how well your body is able to take up sugar. This test is typically done starting when you are 10 years old to make sure that your body is taking up sugar in the right way and involves “fasting” (no eating after midnight until after the test) overnight before doing this test.
Cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET)
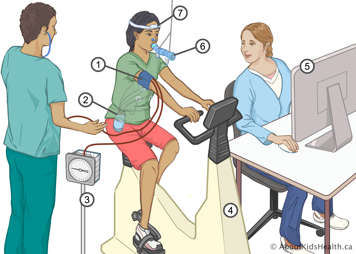
An exercise bike test measures how well your heart and lungs send oxygen to your muscles during exercise. Your heartbeat, blood pressure and oxygen level will be measured while you do this test. This test gives your health-care team a measure of your level of fitness.






